General Surgery
Appendix Surgery

Hernia
Piles Removal
Gall Bladder Surgery
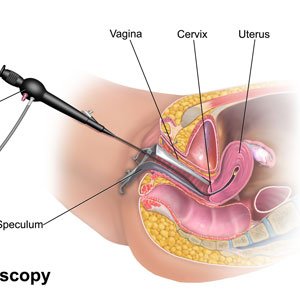
Hysterscopy
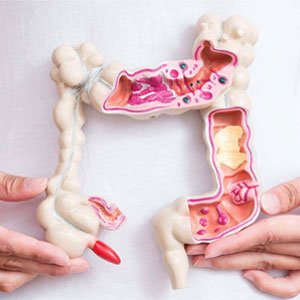
Colon & Rectal Surgery
Mastectomy
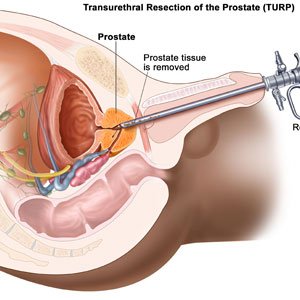
Prostate Surgery
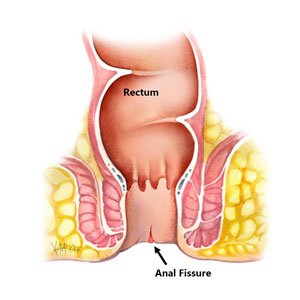
Anal Fissure Surgery
Ovarian Cyst Removal

Breast Surgery
Common Procedures: a. Appendectomy: An appendectomy is the surgical removal of the appendix, typically performed to treat appendicitis, an inflammation of the appendix. b. Cholecystectomy: This procedure involves the removal of the gallbladder and is often performed to treat gallstones or gallbladder inflammation. c. Hernia repair: Hernia repair involves the surgical correction of a hernia, where an organ or tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall. d. Colectomy: Colectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the colon and may be necessary to treat conditions such as colon cancer, diverticulitis, or inflammatory bowel disease. e. Thyroidectomy: Thyroidectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the thyroid gland and may be indicated for conditions such as thyroid cancer or hyperthyroidism.
Risks and Complications: General surgery, like any surgical procedure, carries certain risks and potential complications, including: a. Infection: Infection at the surgical site is a common complication that may require antibiotics or additional treatment. b. Bleeding: Excessive bleeding during or after surgery may necessitate blood transfusions or additional surgical intervention. c. Blood clots: Blood clots can form in the legs (deep vein thrombosis) or travel to the lungs (pulmonary embolism), posing a risk to the patient’s health. d. Anesthesia complications: Adverse reactions to anesthesia, such as allergic reactions or respiratory problems, can occur during surgery. e. Organ damage: In rare cases, nearby organs or tissues may sustain damage during surgery, leading to additional complications.
Recovery Process: The recovery process following general surgery varies depending on the specific procedure performed and the individual patient’s health status. However, some general guidelines include: a. Hospital stay: Patients may need to stay in the hospital for a few days following surgery to monitor for any complications and ensure adequate pain management. b. Pain management: Pain medication may be prescribed to help manage post-operative pain and discomfort. c. Activity restrictions: Patients may need to limit physical activity and avoid heavy lifting for a certain period following surgery to allow for proper healing. d. Follow-up appointments: Follow-up appointments with the surgeon are essential to monitor recovery progress, address any concerns, and remove sutures or staples as needed. e. Gradual return to normal activities: Patients should gradually resume normal activities, such as work and exercise, as advised by their surgeon to avoid complications and promote healing.
